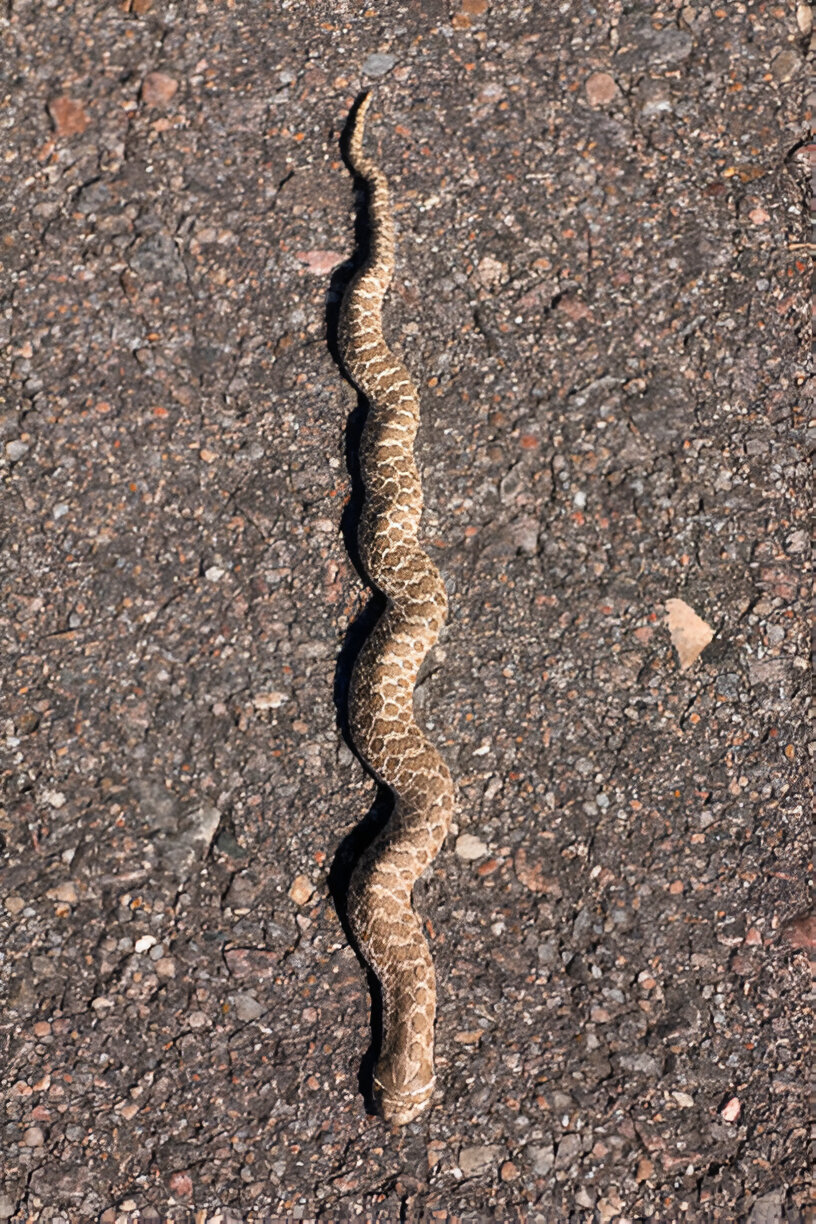
Introduction
Idaho Snakes isn’t just the land of beautiful landscapes and outdoor adventures. Beneath its stunning scenery lies a world teeming with fascinating wildlife, including diverse and intriguing snake species. Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast, an outdoor adventurer, or a resident, understanding the different types of Idaho snakes inhabiting Idaho is crucial for safety and appreciation.
This comprehensive guide aims to inform and educate readers about Idaho’s snake population, offering insights into their habitats, behaviours, and roles in the ecosystem. By the end of this post, you’ll be well-prepared to identify and respect these remarkable creatures during your outdoor pursuits.
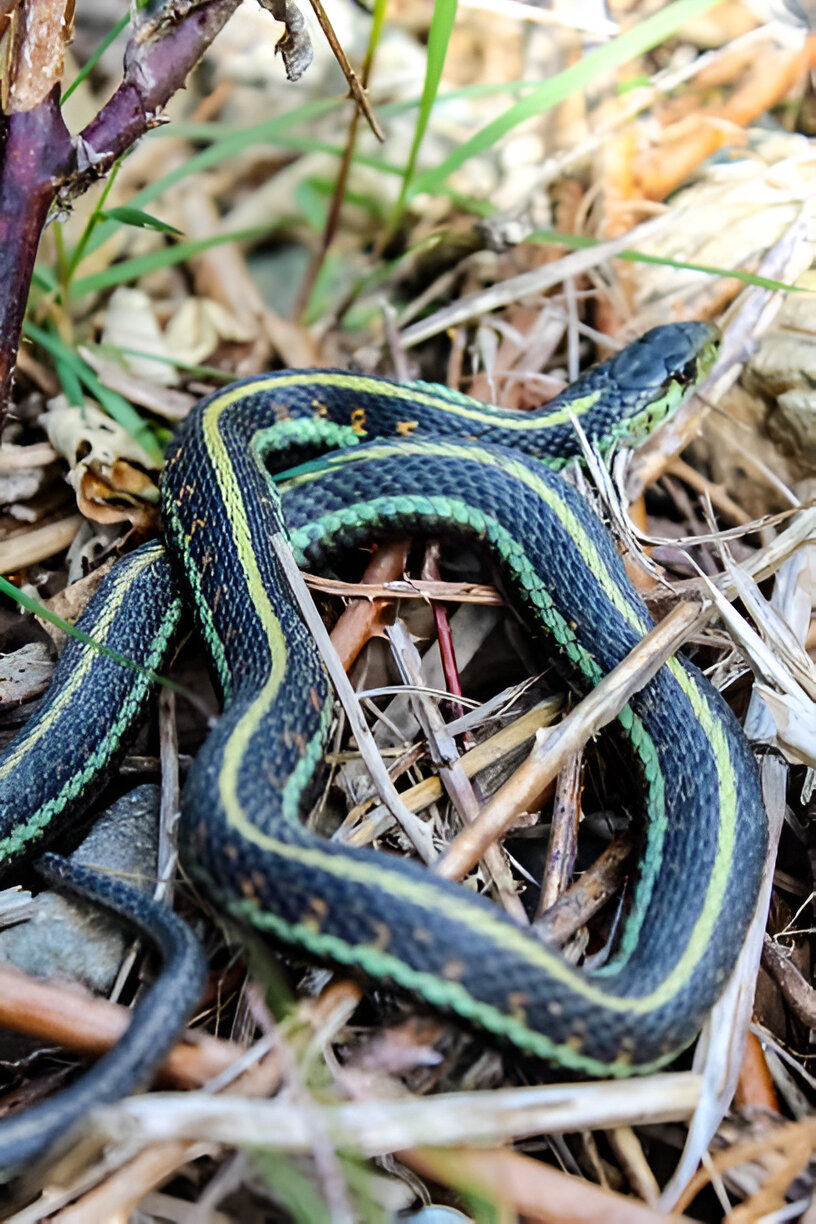
Idaho Snakes: Common Garter Snake (Thamnophis sirtalis)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Common Garter Snake is one of Idaho Snakes most recognizable and widespread snake species. With its slender body, this snake typically features three yellow stripes running down its back on a dark green or brown background. It can grow up to 48 inches long, making it a medium-sized snake.
Typical Habitats of Idaho Snakes
You can often find Common Garter Snakes in areas near water bodies such as ponds, streams, and wetlands. They are also prevalent in meadows and forests. These adaptable snakes thrive in both rural and urban settings, often seen basking in the sun or slithering through the grass.
Behavior and Diet
Common Garter Snakes are diurnal, meaning they are active during the day. Their diet mainly consists of amphibians, small fish, and insects. These non-venomous snakes are known for their docile nature, making them popular pets among snake enthusiasts.
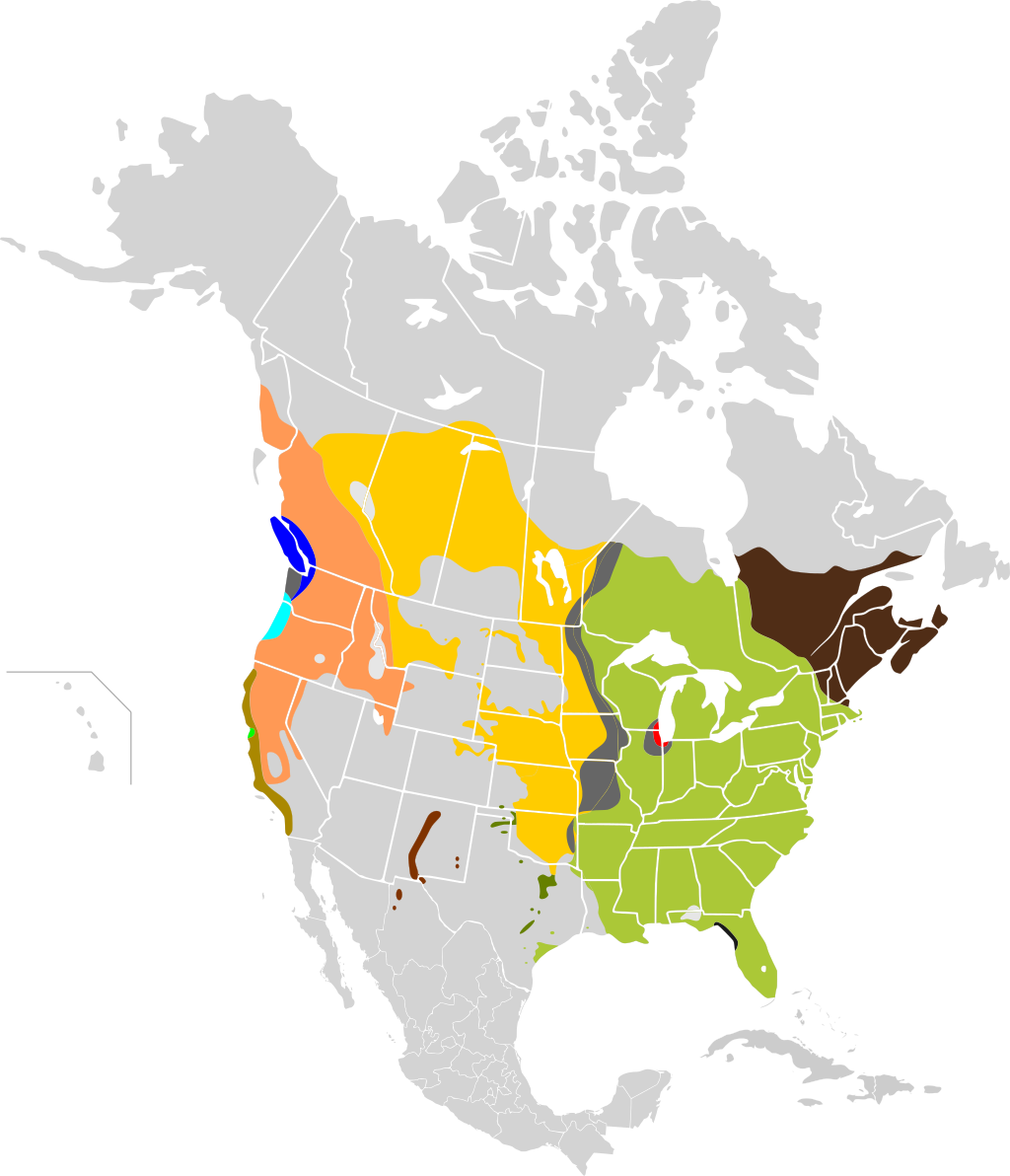
Common Garter Snake Range Map
Discover the Common Garter Snake’s habitat from Canada to Mexico. See where these adaptable snakes thrive in North America’s wetlands, forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
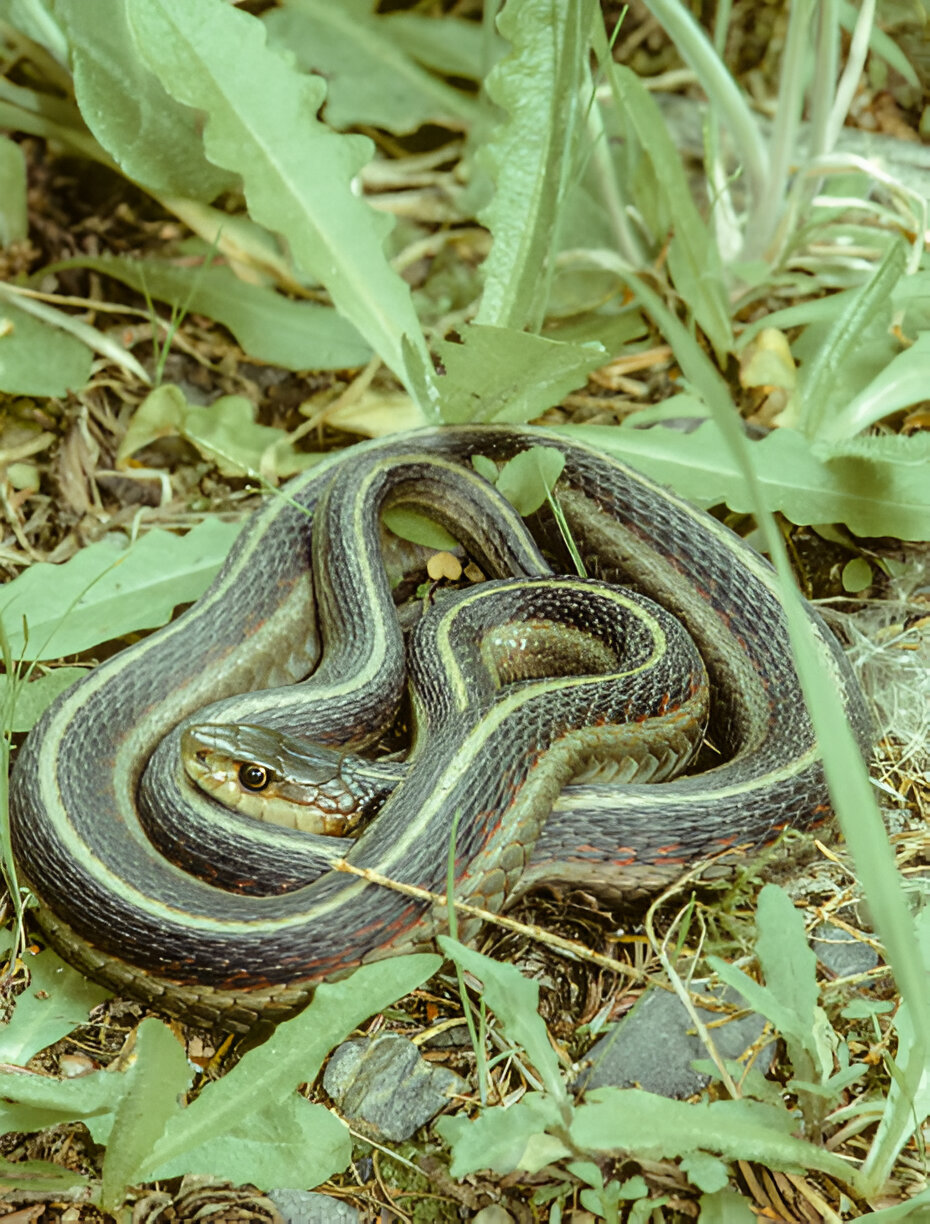
Idaho Snakes: Western Terrestrial Garter Snake (Thamnophis elegans)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Western Terrestrial Garter Snake is another common species found in Idaho, also known as aquatic snakes. It has a more robust build than the Common Garter Snake and can vary in colour from olive to brown with distinctive light stripes. Adults can reach lengths of up to 42 inches.
Preferred Habitats of Idaho Snakes
Western Terrestrial Garter Snakes are versatile and can be found in grasslands, forests, and areas near water. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in various environments, from mountainous regions to urban parks.
Behavior and Diet
These Idaho snakes are known for their opportunistic feeding habits, consuming a variety of prey, including rodents, amphibians, and birds. They are active during the day and are generally non-aggressive toward humans. Their ability to adapt to different habitats makes them one of Idaho’s most widespread snake species.
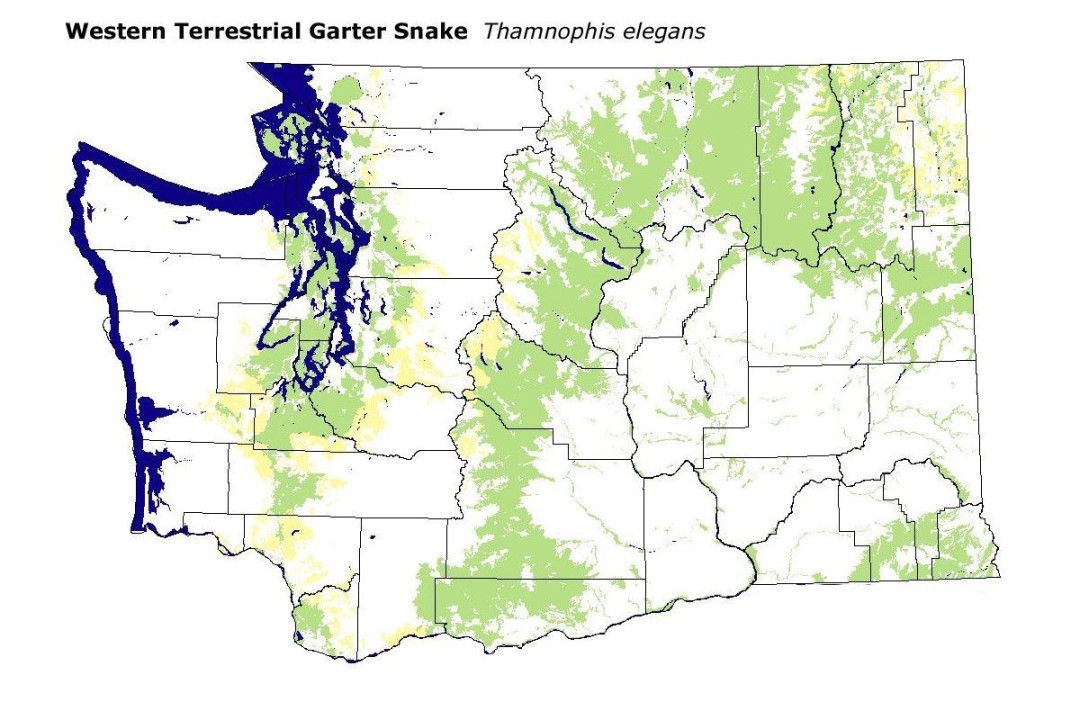
Western Terrestrial Garter Snake Range Map
Uncover the range of the Western Terrestrial Garter Snake across western North America. This species is commonly found in diverse habitats, from coastal regions to mountainous areas, showcasing its adaptability and widespread presence.
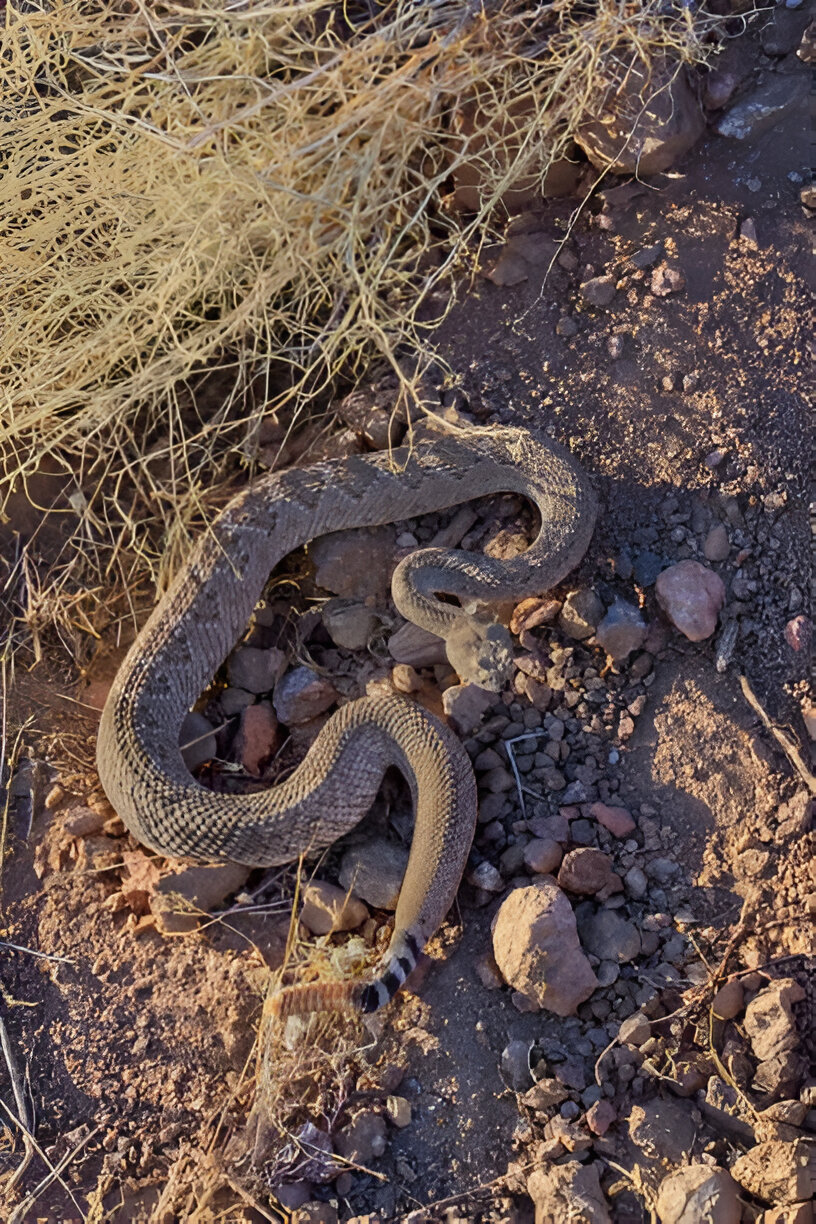
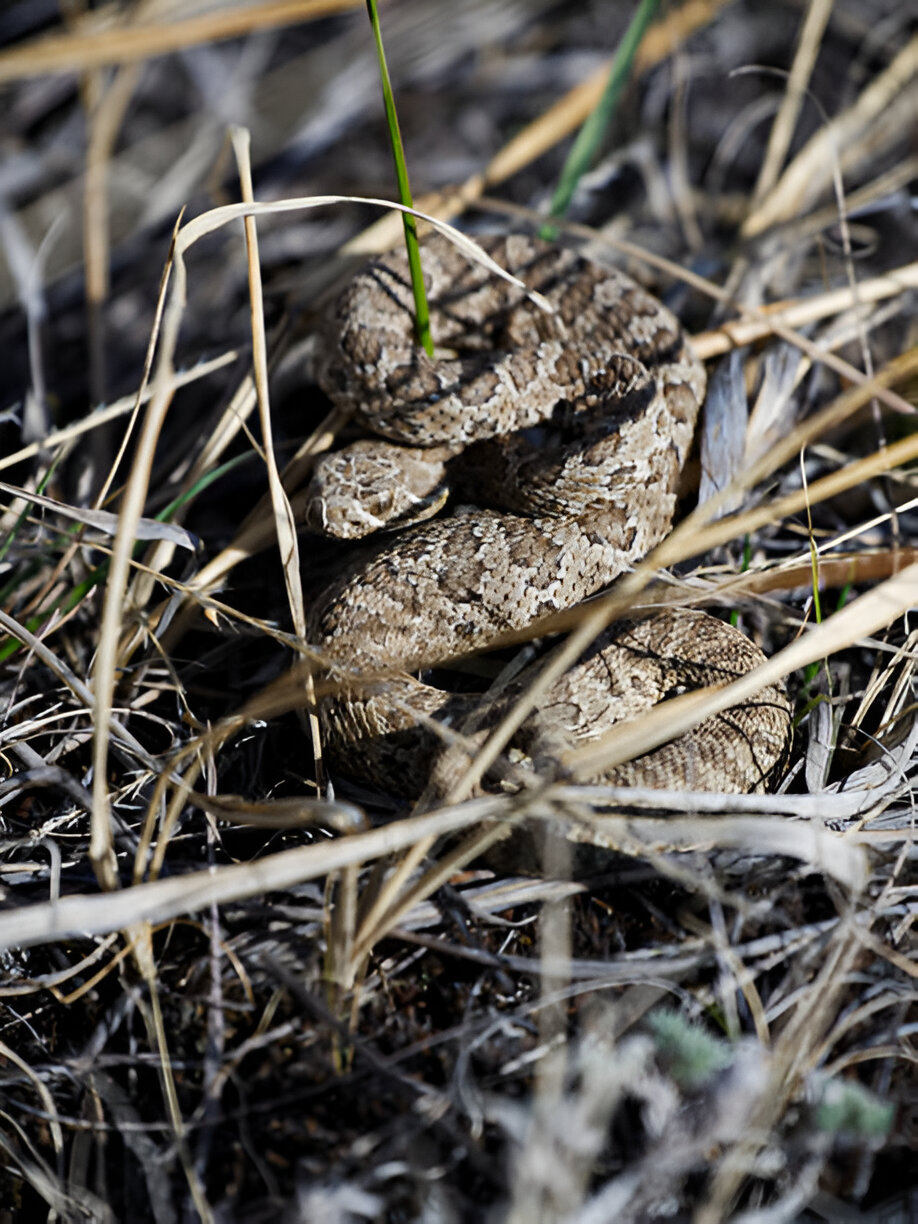
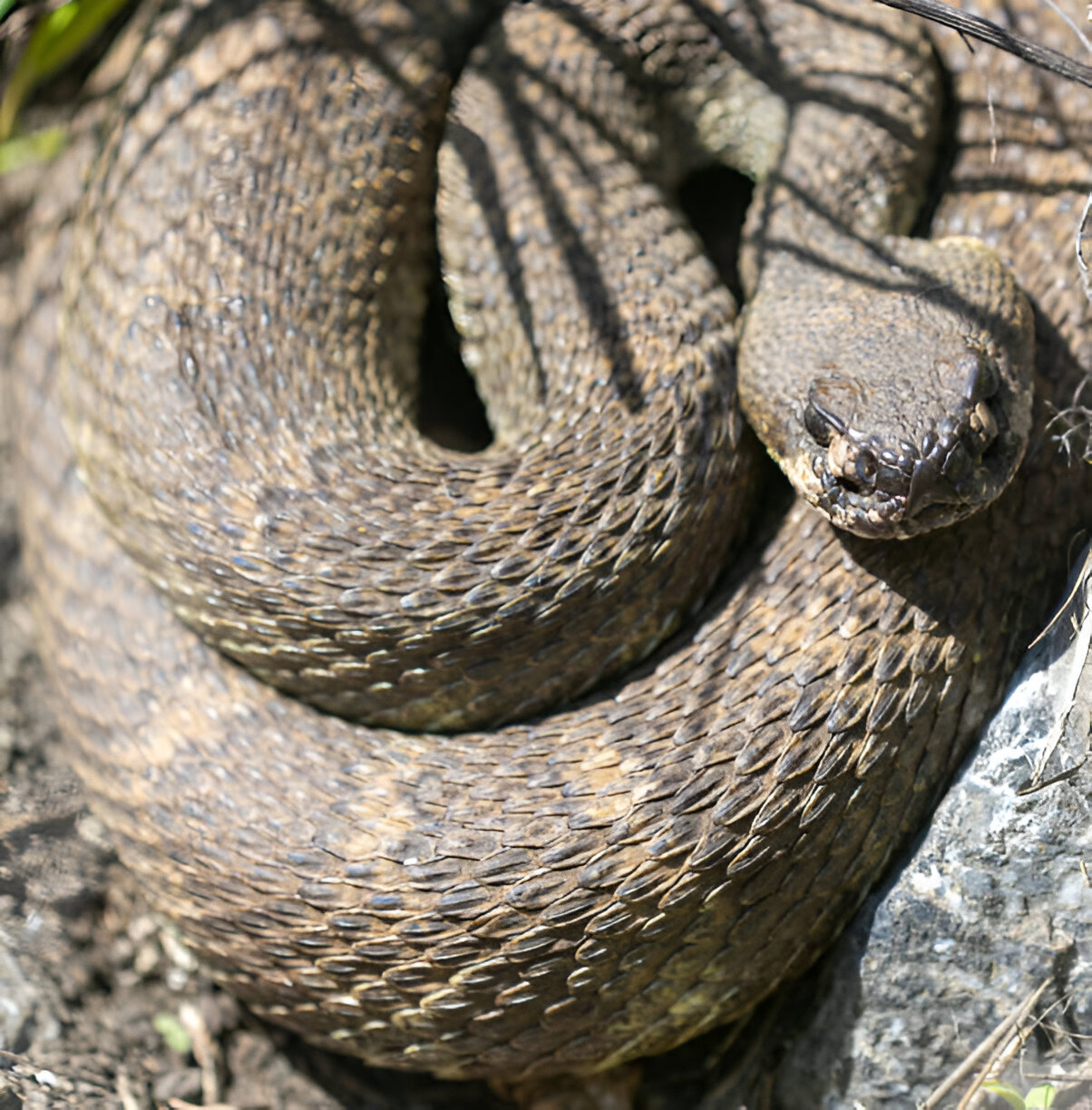
Idaho Snakes: Western Rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Western Rattlesnake is easily identifiable by its distinctive rattle and diamond-shaped head. Its colouration can range from light brown to dark grey, with darker blotches along its back. This venomous snake can grow up to 60 inches.
Preferred Habitats of Idaho Snakes
Western Rattlesnakes inhabit rocky areas, deserts, and grasslands. They prefer arid environments where they can find shelter under rocks or in burrows. These Idaho snakes are often spotted sunbathing on warm, sunny days.
Behavior and Diet
Western Rattlesnakes are ambush predators, lying in wait for prey such as small mammals and birds. They use their venom to immobilize their prey before consuming it. Although their venom is potent, they are generally shy and will only bite in self-defence. If bitten, immediate medical attention is crucial.
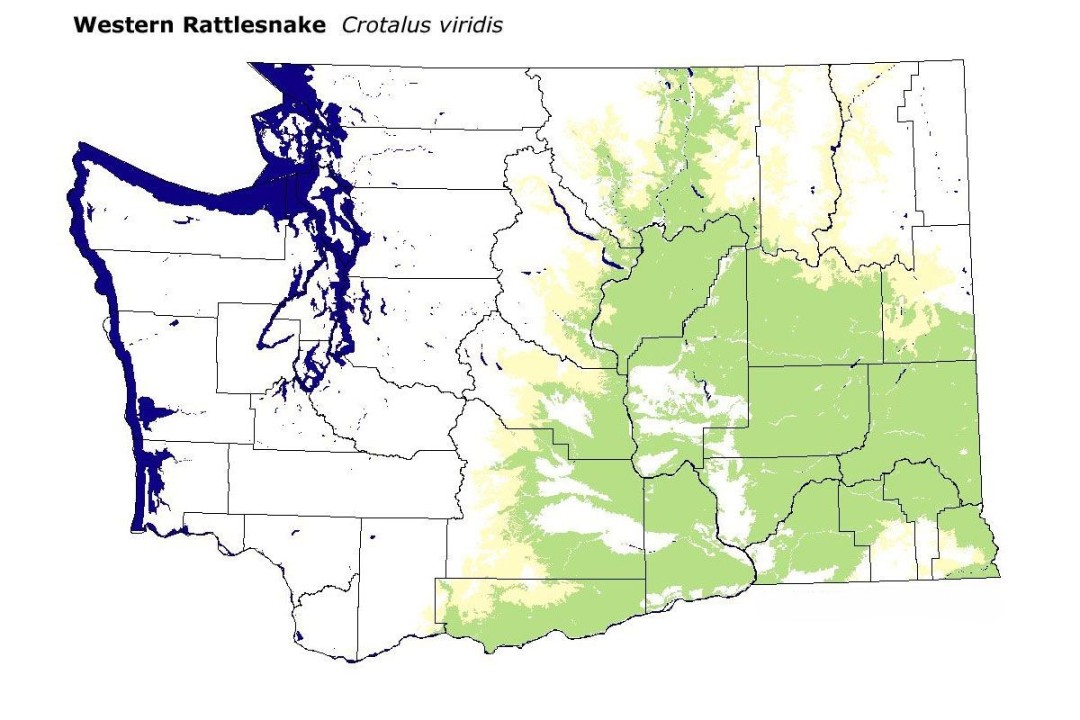
Western Rattlesnake Range Map
Explore the range of the Western Rattlesnake across western North America. This species is frequently found in varied habitats, from arid deserts to forested regions, reflecting its adaptability and widespread occurrence.
Idaho Snakes: Prairie Rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis)
Description and Physical Characteristics
Prairie Rattlesnakes are characterized by their light green to brown colouration and dark, oval blotches along their bodies. Like other rattlesnakes, they have a distinct rattle at the end of their tails. They can grow up to 55 inches in length.
Idaho Snakes Typical Habitats
These Idaho snakes are typically found in central Idaho’s wilderness areas, favouring open grasslands and prairies. They seek out rocky crevices and burrows to escape the heat and predators.
Behavior and Diet
Prairie Rattlesnakes are also ambush predators, feeding on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. They are less common than Western Rattlesnakes but are equally venomous. When encountered in the wild, it’s essential to exercise caution and respect their space.
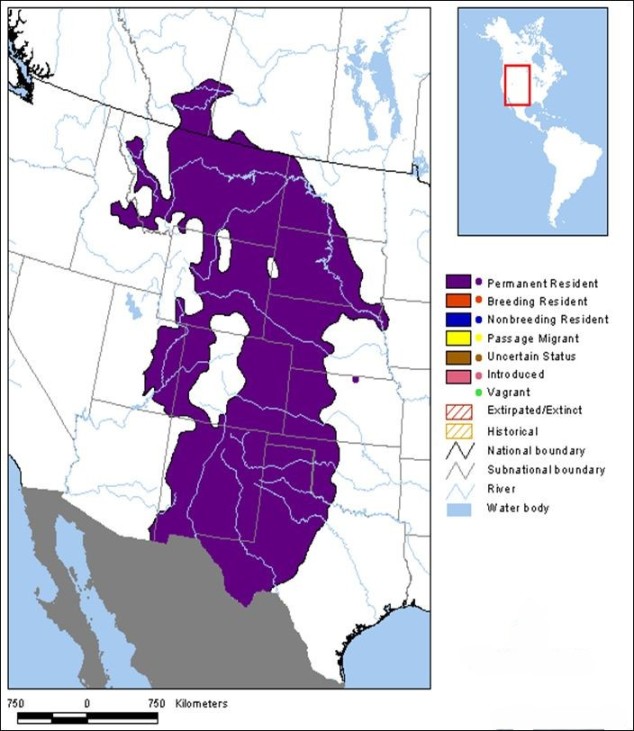
Prairie Rattlesnake Range Map
The Prairie Rattlesnake is found across central North America, inhabiting grasslands, prairies, rocky outcrops, and semi-arid regions. This adaptable species thrives in diverse environments, making it a common sight in its extensive range.
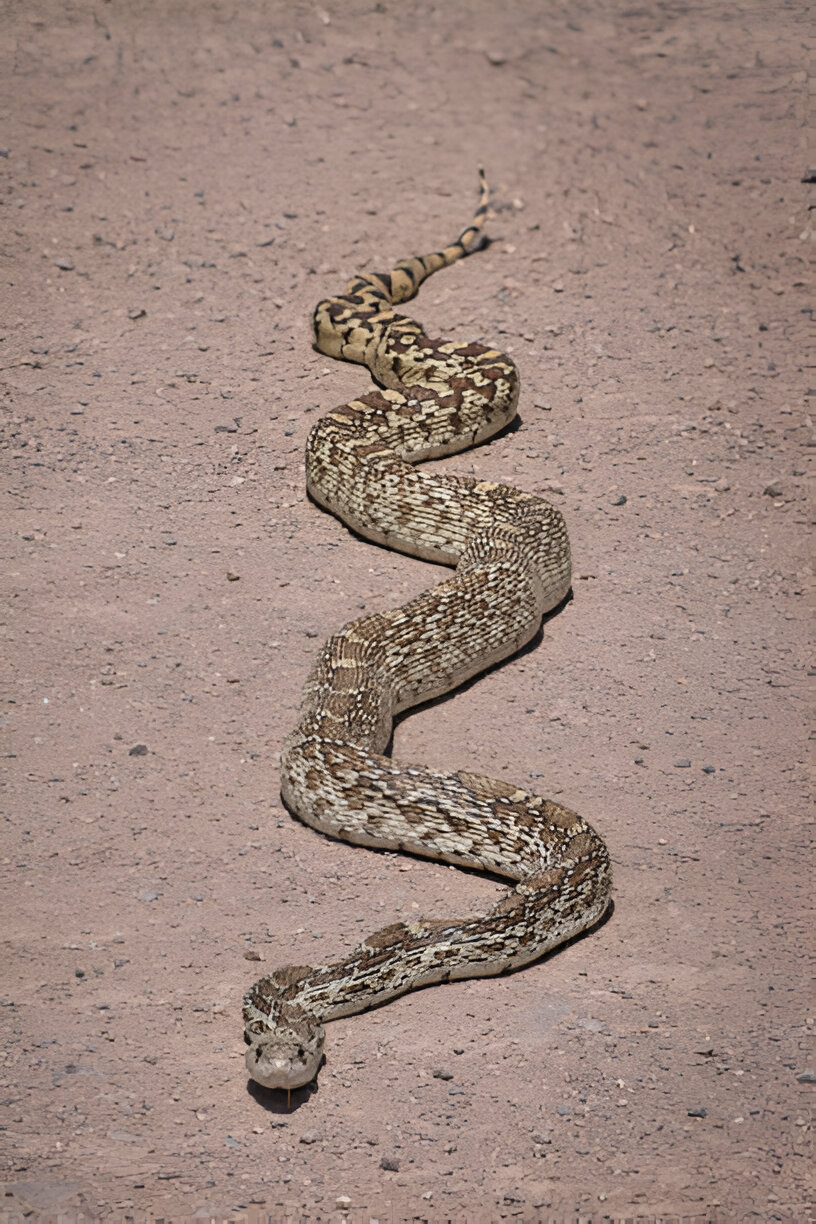
Idaho Snakes: Great Basin Gopher Snake (Pituophis catenifer deserticola)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Great Basin Gopher Snake is known for its striking resemblance to rattlesnakes, which often causes confusion. It has a yellowish-brown body with dark blotches and can grow up to 84 inches, making it one of Idaho’s largest snakes.
Idaho Snakes Habitats
These Idaho snakes thrive in plains, hillsides, and agricultural areas. They are often seen in open spaces where they can easily hunt their prey.
Behavior and Diet
Great Basin Gopher Snakes are constrictors, using their powerful bodies to suffocate their prey, which includes rodents and birds. Despite their intimidating appearance, they are non-venomous and are crucial in controlling rodent populations.
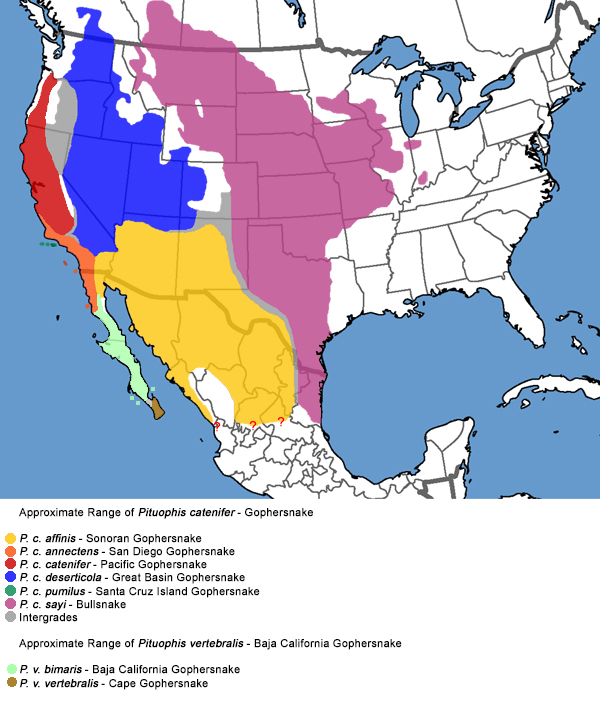
Great Basin Gopher Snake Range Map
The Great Basin Gopher Snake is primarily found in the western United States, inhabiting arid and semi-arid regions. This species thrives in diverse environments such as deserts, grasslands, and scrublands, showcasing its adaptability across its extensive range.
Idaho Snakes: Rubber Boa (Charina bottae)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Rubber Boa stands out with its smooth, rubbery texture and earth-toned colouration. It is relatively small, usually growing to about 33 inches, and its blunt head and tail give it a unique appearance.
Idaho Snakes Habitats
Rubber Boas prefer cool and moist environments, often found in forests, under logs, and in leaf litter. They are also known to inhabit mountainous regions.
Behavior and Diet
These snakes are nocturnal and borrowers, making them elusive and rarely seen. They feed on small mammals and birds, often attacking nests. Rubber Boas are gentle and rarely bite, making them a favourite among snake enthusiasts.
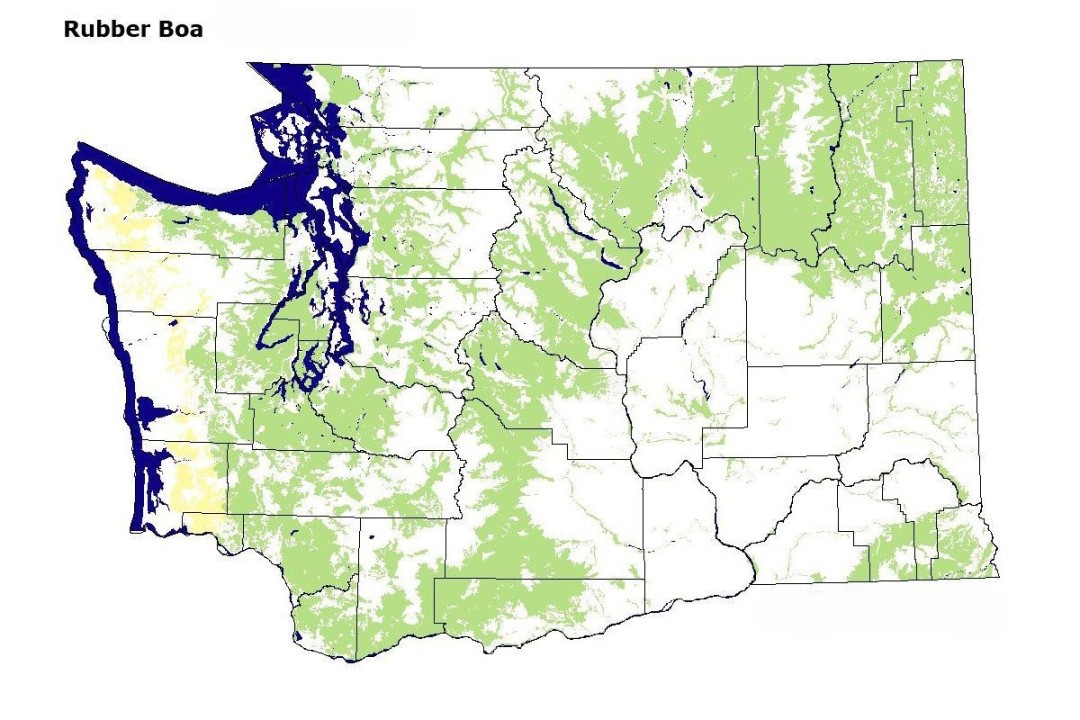
Rubber Boa Range Map
The Rubber Boa is found primarily in the western United States and parts of Canada, inhabiting forests, woodlands, grasslands, and shrublands. This species is known for its adaptability to various habitats within its range.
Idaho Snakes: Northern Pacific Rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Northern Pacific Rattlesnake has a light to dark brown body with distinctive dark bands. Its rattle and diamond-shaped head are key identifiers. They can grow up to 55 inches.
Preferred Habitats
These rattlesnakes inhabit forested areas and rocky outcrops. They seek out sunny spots to bask and can be found in various terrains.
Behavior and Diet of Idaho Snakes
Northern Pacific Rattlesnakes use their venom to hunt small mammals, birds, and amphibians. They are shy and prefer to avoid human contact. If encountered, it’s important to stay calm and back away slowly.
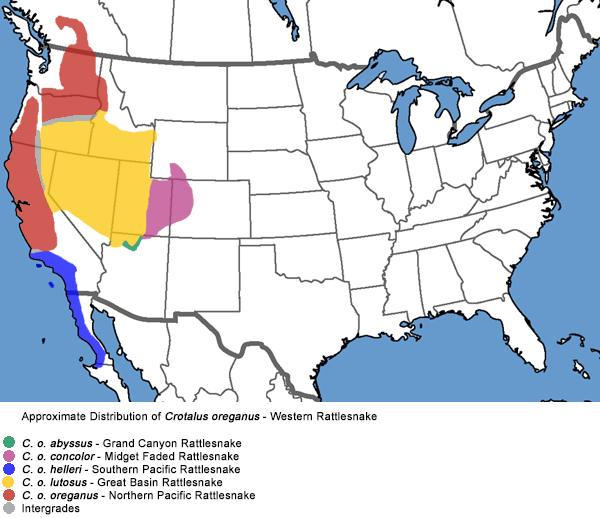
Northern Pacific Rattlesnake Range Map
Found in the western US and parts of Canada, the Northern Pacific Rattlesnake thrives in forests, woodlands, grasslands, and rocky areas.
Idaho Snakes: Western Yellow-bellied Racer (Coluber constrictor mormon)
Description and Physical Characteristics
Western Yellow-bellied Racers are slender, fast-moving snakes with a vibrant yellow belly and greenish-brown back. They can grow up to 60 inches.
Habitats
These snakes are commonly found in open areas and grasslands. They are highly active during the day and prefer sunny environments.
Behavior and Diet
Western Yellow-bellied Racers are agile hunters who prey on small mammals, birds, and insects. Their speed and agility make them effective predators. They are non-venomous and pose no threat to humans.
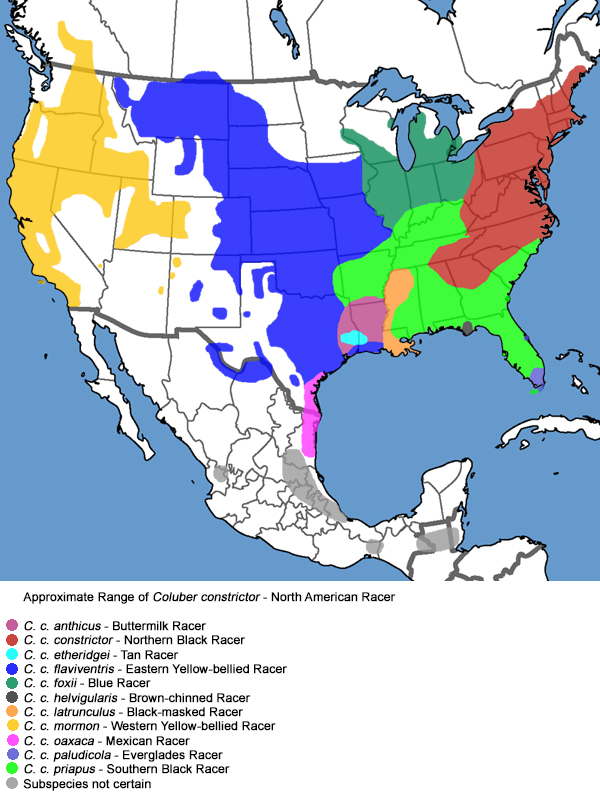
Western Yellow-bellied Racer Range Map
Found in the western US and parts of Canada, the Western Yellow-bellied Racer inhabits grasslands, woodlands, and open forests.
Idaho Snakes: Northwestern Ring-necked Snake (Diadophis punctatus occidentalis)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Northwestern Ring-necked Snake is easily recognizable by the distinctive ring around its neck. It has a small, slender body with a dark back and a bright orange or yellow belly. They typically grow up to 20 inches.
Habitats
These snakes prefer woodlands, moist environments, and areas under rocks and logs. They are secretive and rarely seen.
Behavior and Diet
Ring-necked Snakes are mild-mannered and use their mild venom to subdue prey such as insects and small amphibians. They are non-threatening to humans and add to the diversity of Idaho’s snake population.
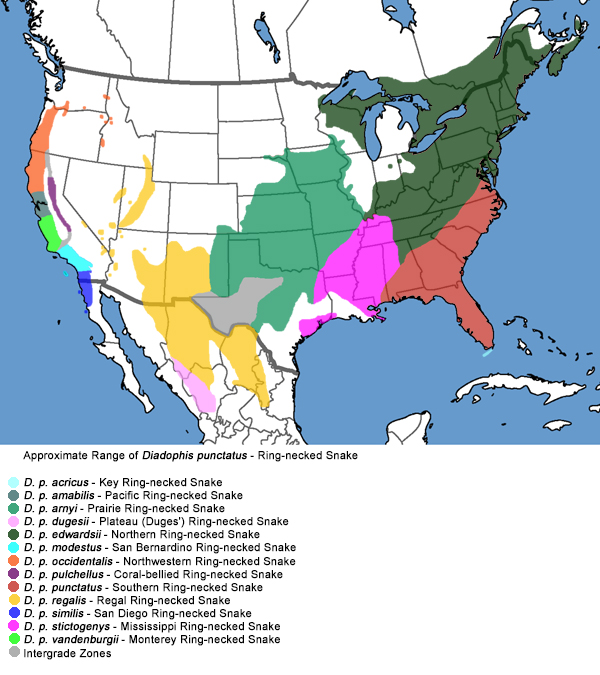
Northwestern Ring-necked Snake Range Map
Found in the Pacific Northwest, the Northwestern Ring-necked Snake thrives in forests, woodlands, and moist habitats. This adaptable species is well-suited to various environments within its range.
Idaho Snakes: Northern Desert Night Snake (Hypsiglena chlorophaea deserticola)
Description and Physical Characteristics
The Northern Desert Night Snake is small and nocturnal. Its body is light gray or brown with dark blotches, and it usually grows up to 26 inches.
Habitats
These snakes inhabit deserts and rocky areas, seeking shelter under rocks and in burrows during the day.
Behavior and Diet
Night Snakes are venomous but not dangerous to humans. They hunt small reptiles and amphibians, using their venom to immobilize prey. Their nocturnal habits make them rarely seen by humans.
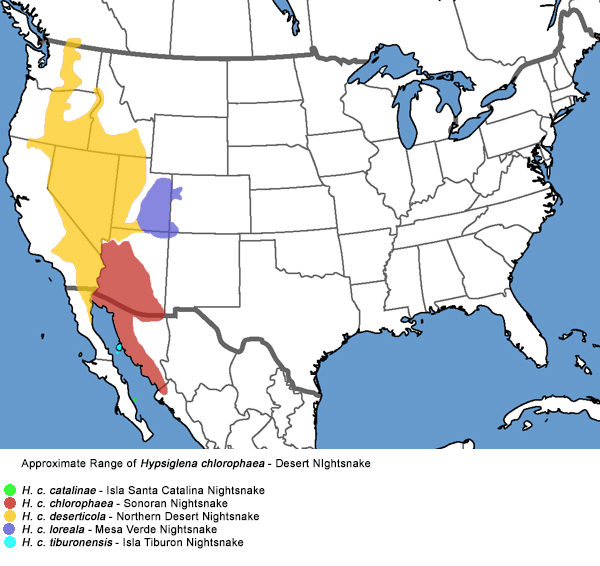
Northern Desert Night Snake Range Map
The Northern Desert Night Snake is found primarily in arid regions of the southwestern US and northern Mexico. This adaptable species thrives in deserts, scrublands, and rocky terrains.
Idaho Snakes: Desert Striped Whipsnake (Masticophis taeniatus taeniatus)
Description and Physical Characteristics
Desert Striped Whipsnakes are long, slender snakes with distinctive stripes running the length of their bodies. They can grow up to 72 inches.
Typical Habitats
These snakes are found in deserts and shrublands. They are highly active and prefer open areas where they can move quickly.
Behavior and Diet
Whipsnakes are active hunters, preying on small mammals, birds, and reptiles. Their speed and agility make them impressive hunters. They are non-venomous and pose no threat to humans.
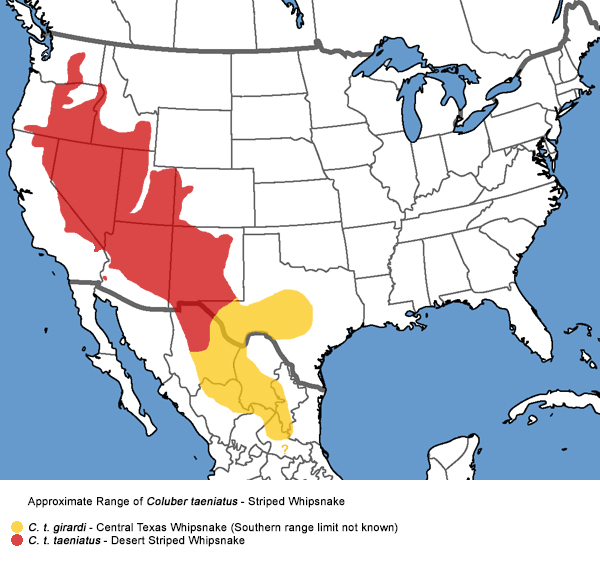
Desert Striped Whipsnake Range Map
The Desert Striped Whipsnake is primarily found in the arid regions of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Known for its adaptability, the Desert Striped Whipsnake thrives in deserts, grasslands, and rocky terrains.
Idaho Snakes: Plains Hognose Snake (Heterodon nasicus)
Description and Physical Characteristics
Plains Hognose Snakes are known for their upturned snout and stout body. They have a variety of colour patterns, usually brown or grey, with dark blotches. They can grow up to 36 inches.
Idaho Snakes Habitats
These snakes prefer sandy areas and grasslands. They are often found in loose soil where they can burrow.
Idaho Snakes Behavior and Diet
Hognose Snakes are famous for their dramatic defence mechanisms, including feigning death when threatened. They prey on amphibians, reptiles, and small mammals. Despite their theatrical behaviour, they are non-venomous and harmless to humans.
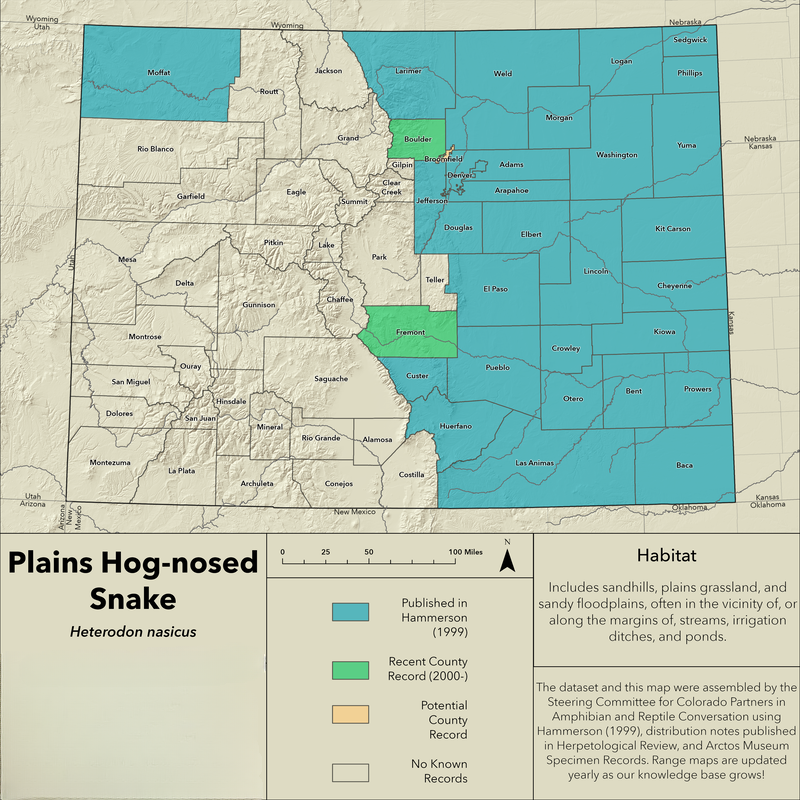
Plains Hognose Snake Range Map
The Plains Hognose Snake is primarily found in the central United States, thriving in grasslands, prairies, and sandy areas. Known for its adaptability, the Plains Hognose Snake flourishes in a variety of habitats within its range.
Idaho Snake is home to a diverse range of snake species, each contributing to the state’s rich biodiversity. Understanding these snakes’ characteristics, behaviours, and habitats is crucial for safety and appreciation. By respecting and preserving local wildlife, we can ensure that these fascinating creatures continue to thrive in their natural environments.
The next time you encounter a snake in the wild, remember to maintain a safe distance and appreciate its vital role in Idaho’s ecosystem. Share your knowledge with others and join local conservation efforts to promote snake conservation and protect their habitats.
FAQ
Q: What types of snakes can be found in Idaho?
Idaho is home to a diverse range of snake species, including:
- Western Terrestrial Garter Snake (Thamnophis elegans): Non-venomous, adaptable, and often near water sources.
- Prairie Rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis): Venomous, found in dry, open areas.
- Rubber Boa (Charina bottae): Non-venomous, smooth, shiny, found in cooler, moist environments.
- Common Garter Snake (Thamnophis sirtalis): Non-venomous, widespread, recognizable by its stripes.
- Mountain King Snake (Lampropeltis zonata): Non-venomous, with striking red, black, and white bands, found in higher elevations.
- Racer (Coluber constrictor): Non-venomous, fast-moving, found in open areas.
- Great Basin Rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus lutosus): Venomous, prefers rocky and arid regions.
- Night Snake (Hypsiglena torquata): Mildly venomous, secretive, found in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Long-nosed Snake (Rhinocheilus lecontei): Non-venomous, burrowing, found in desert areas.
- Ground Snake (Sonora semiannulata): Non-venomous, small, prefers loose soils and dry habitats.
- Striped Whipsnake (Masticophis taeniatus): Non-venomous, agile, found in open and rocky areas.
- Ring-necked Snake (Diadophis punctatus): Non-venomous, small, found in moist environments.
Q: What types of habitats do Idaho snakes prefer?
Idaho snakes inhabit various environments, including forests, grasslands, deserts, and wetlands. Different species adapt to specific habitats like the Western Terrestrial Garter Snake favoring areas near water, while the Prairie Rattlesnake prefers dry, open spaces.
Q: Are Idaho snakes dangerous to humans?
Most Idaho snakes are non-venomous and harmless, such as the Western Terrestrial Garter Snake. However, species like the Prairie Rattlesnake are venomous, so it’s essential to maintain a safe distance and avoid provoking them.
Q: How can I identify Idaho snakes?
Identifying Idaho snakes involves noting their distinct features. For instance, the Western Terrestrial Garter Snake has a yellow or greenish stripe, while the Prairie Rattlesnake features a rattle. Field guides can provide more identification tips.
Q: What is the role of Idaho snakes in the ecosystem?
Idaho snakes control pest populations by preying on rodents and insects, benefiting agriculture and reducing disease spread. They also serve as prey for larger animals, playing a vital role in the food web.
Q: What should I do if I encounter a snake while hiking in Idaho?
Stay calm, back away slowly, and give the snake space. Avoid sudden movements, and do not attempt to handle the snake. Use a walking stick to check areas with tall grass or underbrush.
Q: How can I make my property less attractive to snakes in Idaho?
Remove debris, control rodent populations, seal gaps in buildings, maintain landscaping, and eliminate standing water to discourage snakes from settling on your property.
Q: Are there any poisonous snakes in Idaho?
Yes, Idaho is home to venomous snakes, including the Prairie Rattlesnake and the Great Basin Rattlesnake.
Q: Where are most rattlesnakes in Idaho?
Most rattlesnakes in Idaho are found in dry, open areas such as deserts and grasslands, and they often inhabit rocky regions.
Q: What state has the worst snake problem?
The state with the most significant snake problem is often considered to be Florida, due to its diverse and abundant snake population, including invasive species like the Burmese python.













